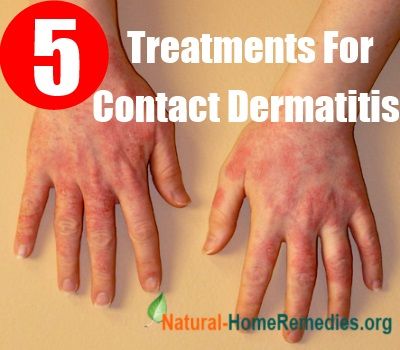
Contact dermatitis is a common type of dermatitis. It can be caused by many reasons, such as allergies or skin care products. Contact dermatitis causes dryness, flaking, redness, and inflammation of the skin. Light skin can turn red, brown, blue, or blackish, while darker skin can turn gray, purple. This condition usually occurs within hours or days of exposure to a strong irritant or allergens.
Contact dermatitis can develop in a wide variety of places, including the inner sides of the hands, lips, or the skin around a blister. It can sometimes be difficult to determine if a person has an allergic reaction to something or if they have actually been exposed to a potentially harmful substance. In such cases, it is best to seek immediate medical attention. Symptoms may include a burning sensation itching and blistering. The skin can also crack or flake off. In rare cases, the skin becomes discolored due to a reaction caused by irritants.
Contact dermatitis is not considered contagious. However, certain precautions should be taken when you are around people who are allergic to allergens and have a history of serious skin conditions. Allergic reactions to allergens include eczema, atopic dermatitis, asthma, food allergies, lupus, seborrheic dermatitis, and urticaria. When a reaction to one of these allergens occurs, it is likely that the other irritants will trigger the person’s allergic reaction.
Some people prone to contact dermatitis tend to itch more often than those who do not. Some people develop contact dermatitis in winter due to exposure to cold temperatures. In other people, contact dermatitis develops from an allergic reaction to the sun’s ultraviolet rays.
Contact dermatitis can affect people of any age, race, gender or sexual orientation. Most children experience this condition but adults can also suffer from it. The most common symptom of contact dermatitis is an itchy rash that often appears on the face, neck and chest. Itching is the body’s way of removing dead cells and other irritants.
If the skin becomes inflamed, it will swell up causing pain and redness. If the rash does not heal in a timely manner, it can turn into sores. That is why it is important to use effective moisturizers when it comes to preventing further damage to the skin. Although most of these products do not contain harsh chemicals, some of them contain a special emollient that softens the skin so that the dead skin cells are pushed out.
Some dermatologist recommend using skin care products to prevent the spread of contact dermatitis. These products include creams and lotions that are designed for use only on sensitive skin. When using these products, they may be recommended by a physician. A physician may also recommend the use of a retinoid cream or antibiotic cream that will help to heal the irritated skin.
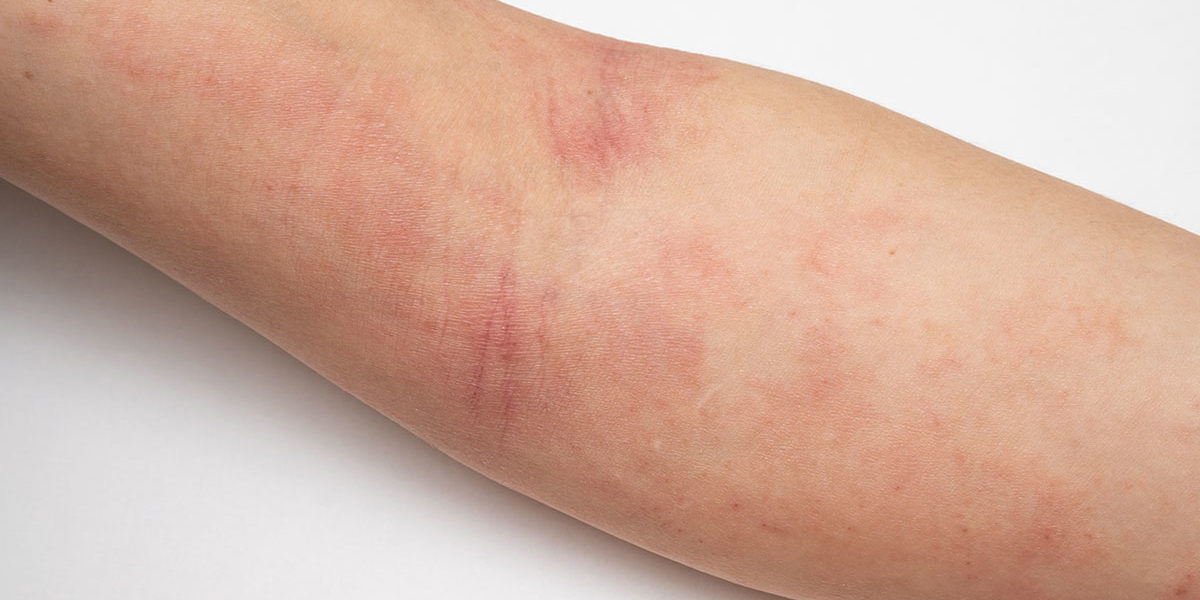
While contact dermatitis is not a very common problem, it can be extremely painful, especially for the children. Some of the symptoms include dryness, redness, irritation and blistering. The most popular products that are used to treat contact dermatitis include medicated ointments and creams that are made specifically for this purpose. Some products are available over the counter but other medications may be prescribed by a physician or dermatologist. Although there are many treatments available, it is essential to visit a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and possible treatment.
While it is difficult for doctors to determine the cause of contact dermatitis, it is believed that it can be caused by an imbalance in the body’s natural oils that are produced by the sebaceous glands. The sebaceous glands produce sebum, which is a natural substance secreted by the sebaceous glands and other skin glands. These glands help to keep the skin hydrated by providing an oily layer to the skin. When the sebum production is overactive, the body’s normal balance of oils produced is affected and causes an inflammatory response that can lead to irritation. As a result, the body may be unable to properly control oil production and the skin becomes excessively oily, flaky, itchy and dry. When the body’s immune system is weak, bacteria can enter the body through broken skin cells and cause the inflammation.
When a dermatologist suspects that you have contact dermatitis, it is important to see the dermatologist for a thorough physical examination. The doctor will look at your skin and possibly take blood tests or a skin culture to determine the cause of contact dermatitis.
In many cases, a combination of medications and various treatments may be recommended to treat the condition. If the diagnosis is not clear, you may be given prescription medications for anti-inflammatory medications and antibiotics.